Today, when technology is developing rapidly, and people are more and more immersed in the world of mobile devices, there is more and more talk that traditional service providers, especially financial ones, will give way to young and more mobile fintech companies (online lenders and neo-banks). In addition to fintech companies that have already become part of the financial services world, we should not forget about large Internet companies, both global (Google, Amazon, Facebook and Apple, so-called GAFA), and local, which have a large share in each separately selected country or group of neighbouring countries, for which financial services are not the main and significant source of revenue. These companies have accumulated a huge client base and an array of information for each client, and they already offer various financial services that were previously considered traditionally banking.
For example, less than a year ago Apple announced the launch of banking card (https://www.apple.com/newsroom/2019/08/apple-card-launches-today-for-all-us-customers/) based on MasterCard payment system and in partnership with the bank Goldman Sachs. Virtual card may be used in the ecosystem of Apple devices and the Apple Pay service, the plastic card issued and linked to the same account may be used at offline points of sale. Similar steps have already been taken by another Internet giant - Amazon, which launched a line of financial products. (https://www.cnbc.com/2019/06/10/amazon-launches-a-credit-card-for-the-underbanked-with-bad-credit.html). Not far behind, Google, announced a partnership with CitiGroup (https://www.coinspeaker.com/google-citi-bank-big-techs/).
In the Russian market, banks and Internet companies also have a rather long history of partnerships, including at the level of the chartered capital.
Earlier in our articles, we have already mentioned what are the key differences of banks and fintech companies in different aspects of their activities. Today we will take a closer look at what the future of online lending may look like in the competition and partnership of fintech companies and banks, especially during crises and other force majeure. We will also look at the role of large Internet players in this process and the place they can take in the financial system.
What are the basic differences between banks, online lenders and large Internet companies, what are the advantages and disadvantages of each of these categories? Let's consider some of them.
Technology
In this case, technologies are understood as the possibility of using, adapting, and introducing a modern technological stack in the operations and productive systems, i.e. real use of these technologies for a wide client audience, and not just in the framework of tests and pilots.
Since fintech companies usually do not have a layer of legacy systems, heavy and expensive to maintain and upgrade, their technology stack in productive systems is more modern and flexible, especially in terms of adding new functionality.
Banks, many of which have been operating on the market for dozens, and some even hundreds of years, operate on older platforms and infrastructure, which are subject to increased regulatory and information security requirements. These constraints reduce the ability to quickly introduce and adapt new technologies for key processes, for example, the process of making a credit decision.
The technological stack of large Internet companies allows, on the one hand, to quickly implement various client services and products, and on the other hand, it is not intended to provide traditional financial and credit services, since the architecture was originally designed for the provision of services of a different type.
The technological flexibility of fintech companies makes it possible to better adapt the product line and the business itself to various constraints and innovations, which can not only remain competitive in a crisis, but also increase the client portfolio.
Audience for lending and other financial services
Fintech companies allow getting access to funds for a wider audience of borrowers. They can lend to borrowers with a higher credit risk in terms of traditional banking risk policies, as well as an audience with moderate or low credit risk, which is difficult to prove their reliability and creditworthiness through traditional data sources. Here we can also talk about the segment of individual entrepreneurs and small and medium-sized businesses, which may require borrowed funds to close the cash gap. Having no large operating expenses and staff, they have the opportunity to offer financial products on better terms.
Banks traditionally lend to borrowers from more premium segments, the risk of which can be assessed using traditional data sources and verification procedures. In addition to that, banks are limited in their ability to take a higher credit risk due to strict requirements on interest rates and reserves.
Internet companies rarely lend to their customers, financial or quasi-financial services are limited mainly by the infrastructure for making payments, in some cases by issuing various payment cards (pre-paid, debit, credit) to pay for purchases, receive cashback, withdraw cash and money transfers.
In times of crisis, when banks usually seriously tighten their policies and requirements for new customers, fintech companies that are not spoiled by premium customers gain access to a whole segment of borrowers with good payment discipline, but no longer meet the more conservative requirements of banks. By providing loans, a better level of service and more individual conditions for the products such customers can stay as fintech company client for a long time.
Channels
Fintech companies are, first of all, a website or a mobile application, which are usually quite simple and functional, providing the simple process of financial service (for example, a loan) application fulfillment. The online office of a fintech company or neo-bank is open 24 hours a day and 7 days a week and is accessible from anywhere in the world if Internet is available. The customer journey, which begins via a tablet or mobile phone right from the couch, is usually more pleasant and easy. In many cases client can do everything on his/her own without getting assistance from the company's staff. In addition, a number of online lenders and all neo-banks issue payment cards, which allow using their services in the offline world.
For a bank, a web-site is a door to a catalog of services offered by the bank and its partners and a list of addresses of the nearest bank offices; you rarely see the opportunity to fulfil an application for a service for a non-client. The mobile application is also focused at the existing client, it can provide a great functionality and a set of services and payments, but for non-customers the application’s functionality is very limited or even absent.
Internet companies provide services through an online channel based on personal accounts in their services and / or social networks, in some cases through the use of native software and / or devices, they do not have offices or branches in the traditional meaning, which makes it easier to obtain services for customers. On the other hand, there may be restrictions on receiving services (for example, Apply Pay works only on native Apple devices).
The ability to receive services online, especially in the current situation that we have seen in the world since the end of 2019, can seriously change the balance of power in the market. In such extreme conditions, online becomes not just a convenient way to attract customers and provide services, but a condition for the survival of the company and the ability to lay the ground for further growth.
Credit application decision process
The speed of decision-making on new customers for fintech companies is much higher than for banks - due to the large amount of data collected, internal and external, due to the real use of powerful technologies and analytical algorithms, it is possible to quickly provide a personalized product and provide a high level of service. This factor is especially important for short loans (for example, the so-called payday loans or PDL), where a borrower needs a decision on a loan and money almost instantly. This also includes the online POS-lending segment for the purchase of various goods, equal payment plans, online instalment loans and online insurance of various categories.
Many banks today offer loans online with a minimum application review time, including pre-approved offers, but this is usually available to existing customers with a client history. For banks, an online channel is the way to access their own client, a shorter way to the services offered, and much less often is a channel for attracting new borrowers. Even if the borrower contacted the bank via the Internet, he would still be sent to the traditional offline decision-making channel, which lengthens the customer journey. In addition to that, banks are required to make a personal identification of the borrower.
Internet companies are not widely presented on the lending market, offering a more convenient infrastructure for making payments and purchases on partner web resources, so in this case there is no need to talk about some kind of decision-making process. Nevertheless, Internet companies have enough capabilities to design a quick decision-making process, since they possess the necessary technologies and a large set of data and knowledge about the client.
So is everything so bad with banks and will they really give way to fintech companies and Internet giants and what can help the banks to compete with both types of companies?
Regulatory requirements and restrictions imposed on banks are also their advantage - they are more resistant to various crises and periods of uncertainty, since each of the banks is under the close supervision of the regulator, and requirements on the capital size and sufficiency therefore they have better chances to reserve the client base, especially during the crises.
Considering the product line, fintech companies mainly specialize in one product where they can provide close to ideal customer journey. Internet companies can offer a wider range of financial services, but have a number of regulatory and technological restrictions on basic financial services. The bank offers a wide range of products and services in one place; traditional banking products remain and will remain the prerogative of banks only - they have a license and the necessary and expensive infrastructure to provide such services. In this case, banks will have access to “long” and cheap deposit money, which means that they will have the opportunity to issue the “long” loan products, which allows them keeping their clients for a very long time.
The third important advantage of banks is the presence of a long history and reputation, which many fintech companies have yet to develop. Reputation allows attracting a new audience in good times and survive in difficult times. There are some cases and a number of countries where large Internet companies also have a high level of reputation and customer confidence due to greater flexibility and a higher level of service, which in combination with the product line and services development may allow them to compete successfully with banks.
There is also a number of other criteria in the table below:
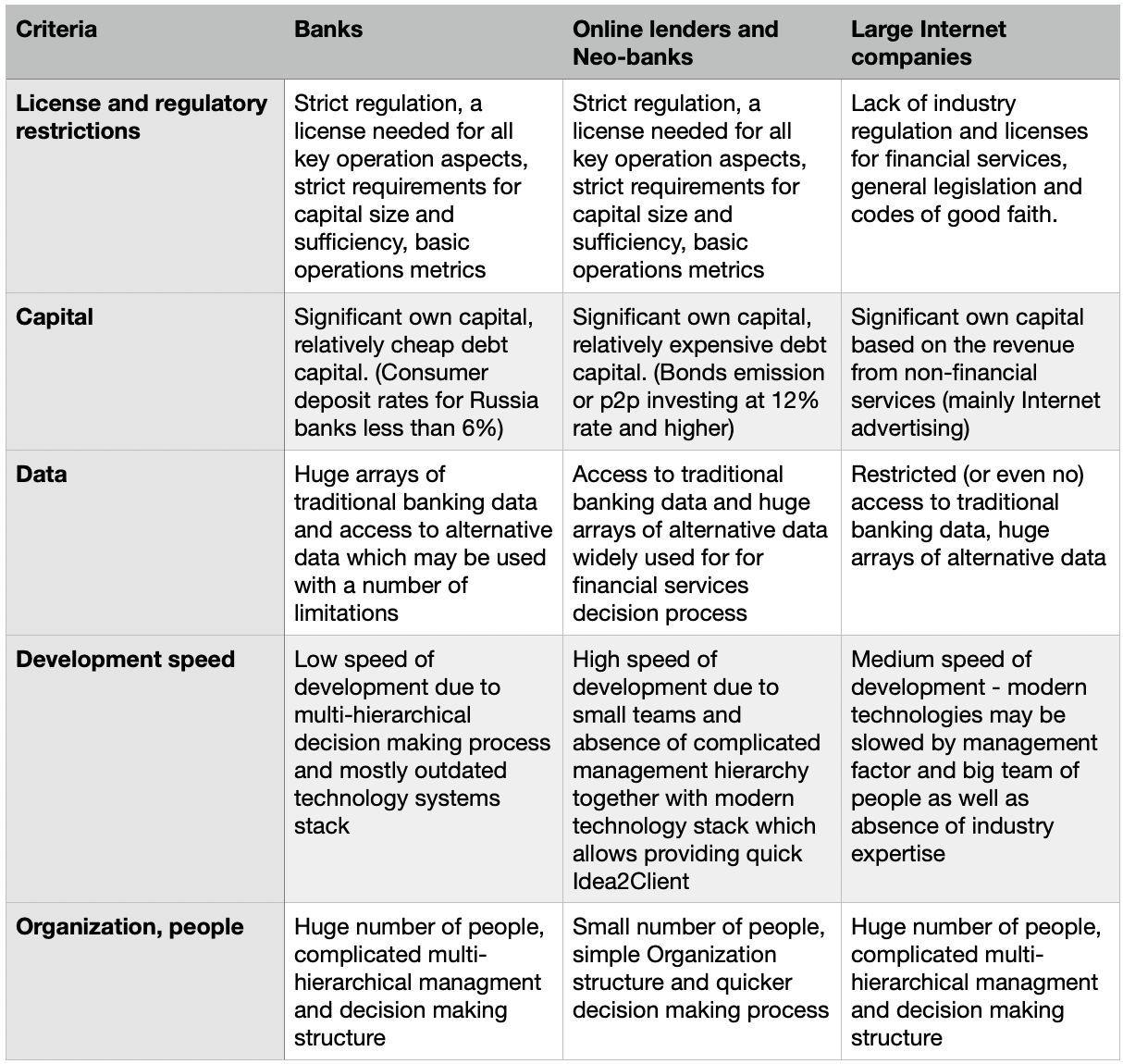
Possible scenarios for the development and interaction of all three types of companies might look like:
- Fintech companies will be able to compete due to further development and implementation of new technologies and data sources, improvement of customer service, as well as attention to operational metrics and regulatory requirements - all this will increase their stability, improve reputation and will be a driver of customer base growth. A higher speed for ecosystem development will be one of the key advantages for fintech companies in the nearest future.
- Banks will actively develop their own technological base and build partnerships both with fintech, and even more so with large Internet companies. Partnership with fintech will allow increasing the flexibility of the decision-making system, faster launch of personalized products and providing more convenient interface to the services; Partnership with Internet companies will allow access to a new audience and higher penetration rate of banking products. At the same time, there will always remain a segment of traditional banking, which is less dependent on technological innovation and prefers personal communication in the office of a financial organization, especially in the segment of premium banking services and a number of other client segments.
- Internet companies already have enormous technological and financial potential, they have sufficient capabilities to compete in the financial services market; their further growth in this market may be associated with increased availability of their services, regulation, especially regarding the use of accumulated data arrays which is not always transparent to clients. Partnership with banks will be one of the ways to resolve issues of regulation and licensing of their operations in local markets. Increasing customer trust will allow to consider such companies not only as an ecosystem for convenient payments and purchases, but also as a substitute for traditional banking services.
Crisis situations that occur with a certain frequency in the world affect the players of the financial world in different ways, and the crisis is an excellent indicator of how the companies operate and develop, the quality and contents of services and the way how they are provided. The fair balance of high-quality and convenient services, technologies, and reputation will allow any company to withstand crisis situations and develop at a double pace in calm times, and attention to the needs of customers during a crisis will strengthen their loyalty and trust.
The future promises to be extremely exciting and interesting ...
